Deep Vein Thrombosis- what are the symptoms of a DVT?
What is a DVT?
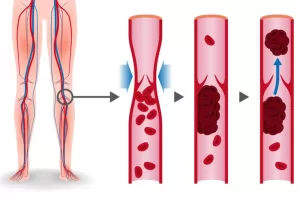
- DVT is short for “ deep vein thrombosis”- this is when a blood clot forms in a deep vein- usually in the deep veins of the calf or thigh.
- Less commonly, a DVT can happen in other parts of the body such as the arm, or abdomen.
- The deep veins of the legs are not the same as varicose veins- the deep veins cannot be seen. However some people with a DVT may also get inflammation of the superficial veins (the ones on the surface of the leg) too.
How do you get a DVT?
Sometimes there is no obvious cause. However, certain factors can increase your risk of getting a DVT. These include any conditions that make the blood more likely to clot, or situations where your mobility is reduced for one reason or another. The following are known risk factors for DVT
- Recent surgery
- Recent fractures or orthopaedic (bone) surgery- especially involving the legs
- Long haul flights ( sometimes called “economy class syndrome”), or other long journeys by train, bus or car.
- Smoking
- Obesity (a body mass index or “BMI” > 30)
- Dehydration
- Pregnancy
- The oral contraceptive pill and HRT (hormone replacement therapy)
- Cancer
- Damage to the vein- due to previous DVT, chemotherapy, injections including drug abuse, vasculitis.
- Nephrotic Syndrome
- Genetic conditions that increase clotting risk- e.g Factor V Leiden
- Antiphospholipid Syndrome
What are the symptoms of a DVT?
A DVT in the leg may have no obvious signs, but common symptoms of a DVT include:
- Calf swelling
- Calf tenderness or pain
- Redness of the calf and increased warmth to touch
Sometimes a DVT first shows up with complications, which can be serious, even life-threatening.
What are the complications of a DVT?
As a clot grows larger, some pieces may break off and travel to other parts of the body. The most common complication is a “pulmonary embolism” or “P.E”. This is when a clot lodges in the lungs. A large P.E can cause instant collapse and death, but in many cases will first show up with the following symptoms:
- Shortness of breath
- Pleuritic chest pain (sharp chest pain which is worse or “catch” when you take a deep breath)
- A dry cough
- Coughing up blood
What should you do if you have symptoms of a DVT?
- If you think you may have symptoms of a DVT, it’s essential to seek immediate medical attention as it can be a life-threatening condition.
- Your doctor may advise blood tests (called d-dimers), an ultrasound scan of the leg, or even a scan of the chest if a P.E is suspected.
- You may need to attend an emergency department.
- If a DVT or PE is confirmed, blood thinners or “anticoagulants” can be started which stop the clot growing, and help to prevent further serious complications.
How can you prevent DVT?
- Risk of developing a blood clot is reduced by maintaining a healthy weight, not smoking, and staying well hydrated.
- If you are on the contraceptive pill, speak to your doctor to make sure you’re on one of the lower risk options.
- If going on a long journey, avoid prolonged sitting (e.g. by taking walks up and down the aisle of the plane), and avoid alcohol and sedative medications- this is especially important if you’re on the contraceptive pill or if you’re a smoker.
- If you have had a DVT in the past, it’s even more important to avoid other risk factors.
- Some people opt to wear compression stockings during flights- but it’s important that these fit correctly.
- If you have had recent surgery, it’s good to be mobile afterwards as soon as you can (as per your doctor’s advice).
If you develop symptoms of a DVT or PE, particularly following surgery or a period of immobility, it’s essential you see a doctor immediately.
Cosmetic surgery
What is cosmetic surgery? Cosmetic surgery is an operation that is done to your face or body to improve its appearance or function. It is performed because you desire [...]
Why am I sweating at night?
Why am I sweating at night? If you regularly wake up with your pyjamas or sheets drenched in perspiration for no apparent reason, you’re probably experiencing night sweats. While [...]
ITB syndrome
ITB syndrome Iliotibial band syndrome, also referred to simply as ITB, is a common condition that causes knee and leg pain. In some studies it can affect up to [...]