☉ Doctors online now - 15 minute priority booking available
Gout- 6 things that may reduce attacks
What is Gout?
- Gout is a form of arthritis caused by formation of uric acid crystals around the joints.
- Uric acid is produced, in part, from the breakdown of certain foods in the body.
- Uric acid usually passes out of the body through the kidneys, but in some people this process is slower and less efficient.
- This can allow uric acid levels to build up in the bloodstream (particularly if certain foods are eaten)- then crystals form in the joints and symptoms of gout arise.

What are the symptoms of Gout?
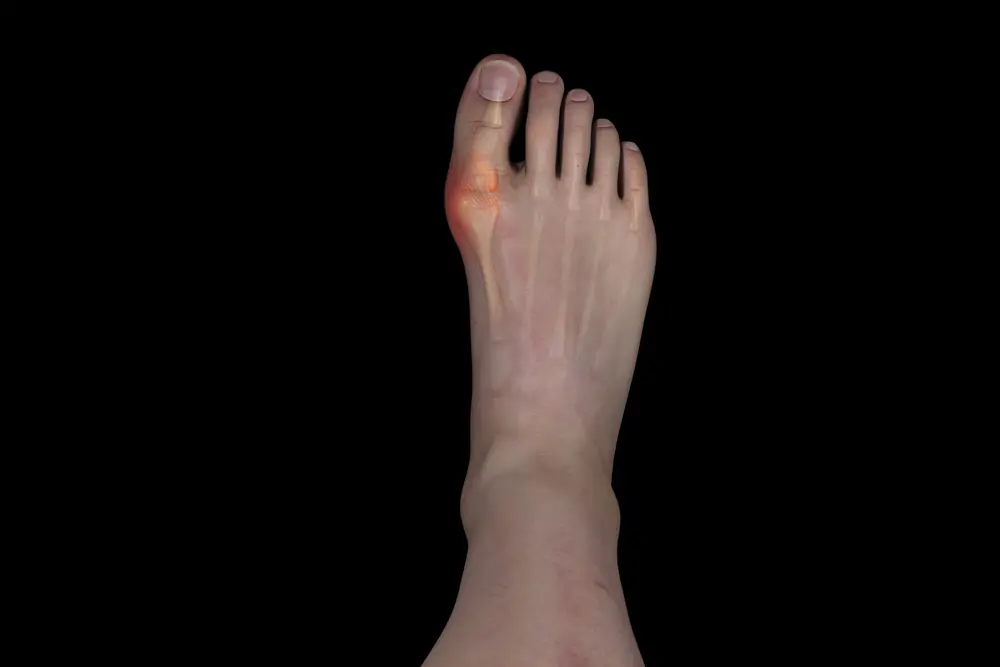
- Common symptoms of gout include pain, heat, swelling and redness around the affected joints
- The most common joint affected by gout is at the base of the big toe (around the ball of the foot)
- However, other joints can be affected- including elbows, knees and ankles.
- Some people develop “tophi”- these are hard nodules under the skin, often around affected joints.
How is Gout diagnosed?
- A doctor can usually make the diagnosis based on the typical symptoms of gout
- Blood tests may also be requested. Urate levels may be high. A full blood count may show raised white cells caused by inflammation, and inflammatory markers such as ESR and CRP may be higher than usual.
- Xrays are not usually needed, but if done may show a typical appearance of gout.
Treatment for Gout
Lifestyle changes
- If you are overweight, gradual weight loss can lower uric acid levels and reduce the risk of gout attacks. But more extreme fasting or ‘crash’ dieting, can actually increase uric acid levels and trigger a gout attack, so it’s important to slim down gradually.
- Certain foods contain high levels of substances known as “purines” that get broken down to uric acid in the body. If you have gout, these should be avoided or taken in low amounts . Purine-rich foods include:
- meat (particularly red meat and offal, such as liver, kidneys and heart)
- seafood (particularly shellfish, scallops, herring, mackerel, sardines, anchovies)
- foods containing yeast such as Vegemite and beer
- Alcohol can increase your risk of a gout attack as it can raise the uric acid levels in your blood. Try to reduce the amount of alcohol you drink and avoid binge drinking. It seems that gout attacks are more common in beer and spirits drinkers than in people who drink wine.
- Sweet fruit juices can also trigger symptoms of gout and should be avoided.
- Dehydration (not drinking enough water) may be a risk factor for gout although this is not well proven in research. Drinking 1.5 – 2 litres of fluids a day is recommended for general health benefits. However if you are taking diuretics (also known as ‘water pills’ or tablets which help the body get rid of water) or have heart or kidney problems, talk to your doctor first.
- If you also have high blood pressure, certain blood pressure medications may actually reduce symptoms of gout- ask your GP or pharmacist for advice.
Medication for Gout
- Preventive medication for gout should be considered if you get more than 2 gout attacks per year.
- For flare ups, your doctor may recommend treatments such as anti-inflammatories or oral steroids.
- If you’re on medications for other health issues, such as high blood pressure, discuss them with your doctor to make sure that they are not making your gout worse (e.g. diuretics/water tablets)
If you have further questions about the symptoms of gout, or the various treatment options, speak to your GP.
Getting a Mental Health Care Plan in Australia: Your Guide
Getting a Mental Health Care Plan in Australia: Your Guide Mental health matters—and if you’re feeling overwhelmed, anxious, or down, a mental health care plan can help. But what is it, and how do [...]
UTI Symptoms and Treatment: What You Need to Know
UTI Symptoms and Treatment: What You Need to Know Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are common, uncomfortable, and often disruptive. But what exactly are the signs to watch for, and how can you get relief [...]
Free Mental Health Care Plan Online | Bulk-Billed by Qoctor
Free Mental Health Care Plan Online | Bulk-Billed by Qoctor Discover how to get a free, bulk-billed Mental Health Care Plan (MHCP) in Australia through Qoctor's telehealth service. Accessing [...]