Eustachian Tube Dysfunction- blocked ears
If you’ve ever had the sensation that your ears are blocked, or you feel you need to pop them but they just won’t pop, you may have had “Eustachian Tube Dysfunction”. It’s a common problem, and one that often brings people to see the doctor. So, what are Eustachian Tubes, what’s their role and what causes them to misbehave?
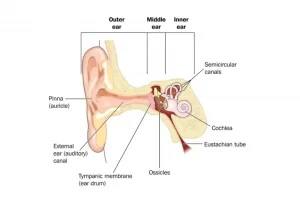
What are the Eustachian Tubes?
- The Eustachian Tubes are thin channels or tubes that connect the middle ear (the part of the ear behind your eardrum) to narrow openings high up in the back of the throat, behind your nose.
- The purpose of these tubes is to equalise the air pressure in the middle ear with the air outside, and to allow any fluid or mucus in the middle ear to drain away.
- Normally, the Eustachian Tubes open for an instant when you chew, swallow, yawn, or if you purposely pop your ears by blowing out against a tightly closed mouth and blocked nose. Usually, you’ll hear a little clicking sound as the Eustachian Tubes open and shut.
What happens if the Eustachian Tubes are blocked?
- If the Eustachian Tubes tubes get blocked for one reason or another, the air pressure either side of the eardrum becomes unequal, making it harder for the eardrum to vibrate properly and sometimes leading to a build-up of fluid or mucus in the middle ear.
What are the symptoms of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
Symptoms of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction include:
- Blocked ears
- Reduced or dulled hearing
- An itchy or tickly sensation in the ears
- Tinnitus (ringing or buzzing in the ears)
- A sense of needing to pop your ears but not being able to
- Crackling or popping sounds in the ears
- Pain or discomfort in the ears
What causes Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
There are several health issues that can trigger Eustachian Tube Dysfunction, including:
- Head colds or other respiratory viruses- mucus blocks the tubes or the place where they open into the back of the throat
- Sinusitis-a postnasal drip occurs when there is mucus flowing down from the back of the nose, into the throat. This mucus may cover the opening of the eustachian tubes.
- Hay fever or other allergic rhinitis – again, mucus production can lead to blockage of the tube openings
- Anything that causes rapid changes in air pressure and/or altitude- e.g. air travel, climbing mountains, using an elevator in a tall building.
- Smoking- this irritates the airways and the “cilia” which are tiny protective hair-like structures that clear out the middle ear.
- Obesity- fatty deposits may cause congestion around the eustachian tubes
Who gets Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
- Anyone can get it, but it’s more common in kids, as their tubes are smaller and narrower. Children also naturally get more viral illnesses, as their immune systems are still maturing.
- People who fly a lot may also be prone to it.
- And as mentioned above, smoking and obesity may increase symptoms.

What is the best treatment for Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
In many cases, symptoms of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction get better after a few days, without any treatment.
Depending on the cause, things that may help include:
- Using a decongestant spray if you have a head cold ( to reduce mucus and postnasal drip)
- Using an antihistamine and/or steroid nasal spray if you get hay fever (you may need to use these long term, depending on whether your hay fever is seasonal or year-round)
- Chewing gum, drinking water, and purposely “popping” your ears may encourage the Eustachian Tubes to open, offering some relief.
- Blowing up balloons may help!
- Stop smoking
- If you’re overweight, losing weight may help
When should you see a doctor?
If your symptoms continue for more than 2 weeks or so, you should see your doctor for a check-up. However, if you develop symptoms such as severe earache, headaches, dizziness, vomiting, fever, dramatically reduced hearing, or if you feel particularly unwell, you should seek immediate medical attention.
What else causes blocked ears?
There are other conditions that can lead to a sensation of blocked ears, including:
- Ear wax
- Middle ear infection (otitis media)
- Infection of the outer ear canal (otitis externa or swimmer’s ear)
- Very rare causes such as tumours or stroke
If you have blocked ears, or other symptoms relating to your ears, you should speak to your doctor.
Getting a Mental Health Care Plan in Australia: Your Guide
Getting a Mental Health Care Plan in Australia: Your Guide Mental health matters—and if you’re feeling overwhelmed, anxious, or down, a mental health care plan can help. But what is it, and how do [...]
UTI Symptoms and Treatment: What You Need to Know
UTI Symptoms and Treatment: What You Need to Know Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are common, uncomfortable, and often disruptive. But what exactly are the signs to watch for, and how can you get relief [...]
Free Mental Health Care Plan Online | Bulk-Billed by Qoctor
Free Mental Health Care Plan Online | Bulk-Billed by Qoctor Discover how to get a free, bulk-billed Mental Health Care Plan (MHCP) in Australia through Qoctor's telehealth service. Accessing [...]