Medically Reviewed by Dr Davinder Nagah
Last updated on 13.06.2024
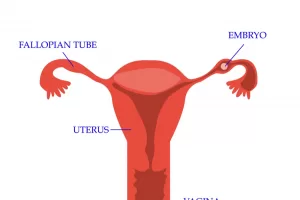
What is an Ectopic Pregnancy?
- An ectopic pregnancy is when a fertilised egg does not implant in the wall of the uterus (womb) as it should, but attaches somewhere else.
- Most ectopic pregnancies occur in one of the fallopian tubes, or less frequently, in the ovary, along a caesearean section scar, or in some other part of the tummy (for example, on the bowel).
- In almost all cases the Ectopic Pregnancy cannot develop a proper blood supply- the fallopian tube is not able to support the growing embryo, so it cannot survive.
- Ectopic pregnancy needs to be quickly diagnosed and treated, as rupture and internal bleeding can occur.
How common is Ectopic Pregnancy?
It occurs in around 5 in 1000 pregnancies.
What are the symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy?
- Ectopic Pregnancy can be difficult to diagnose, as the symptoms may not be obvious.
- At first, it may seem like a normal pregnancy- a missed period, morning sickness and tender breasts.
- In some cases a woman may not even know she is pregnant until she gets symptoms of an Ectopic Pregnancy.
- As the pregnancy develops, quite soon there may be pelvic pain, lower back pain or lower abdominal pain- quite often this pain will be towards one side of the tummy. There may also be unexpected vaginal bleeding or spotting, but not always.
- As an Ectopic Pregnancy continues to grow, it can cause sudden rupture (bursting) of a fallopian tube, and internal bleeding which can be life-threatening. This can present with sudden severe lower abdominal pain and shock (low blood pressure and a rapid pulse).
Is Ectopic Pregnancy serious?
If the fallopian tube ruptures (which happens in about 15% of Ectopic Pregnancies), it can lead to severe pain, internal bleeding and shock. This is a medical emergency.
What are the risk factors for Ectopic Pregnancy?
Certain factors can increase the risk of having an Ectopic Pregnancy. Blockages or scarring in the fallopian tubes can prevent an egg moving to the uterus, resulting in implantation in the tube. There are tiny hairs in the fallopian tubes that move the fertilised egg towards the uterus- if these hairs are not working properly, Ectopic Pregnancy can also occur.
Issues that can increase the risk of Ectopic Pregnancy include:
- previous Ectopic Pregnancy
- history of pelvic infection , including pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) caused by STIs such as chlamydia.
- Endometriosis
- defects of the fallopian tube
- assisted reproduction
- damage to the fallopian tube caused by a ruptured appendix or other pelvic surgery
How is Ectopic Pregnancy diagnosed?
- about 15% of cases are diagnosed when there is sudden rupture, often in the setting of an Emergency Department.
- Diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy is usually made by physical examination, blood tests, ultrasound scans and/or keyhole surgery.
What is the treatment for Ectopic Pregnancy?
- If an Ectopic Pregnancy is not treated it can lead to internal bleeding and can become life-threatening. Treatment options depend on the individual case, but can involve medication or surgery.
- If a fallopian tube has already ruptured and/or there is internal bleeding, emergency surgery will be performed, as this is a life-threatening situation. A blood transfusion may be needed.
- If the doctors think the risk of rupture and internal bleeding is quite high, they may advise surgery.
- If the Ectopic Pregnancy has not caused rupture of a tube, and the risk of internal bleeding is thought to be low, medication may be used to stop the Ectopic Pregnancy from growing. This does not always work, in which case surgery is the next option.
What about future pregnancies?
- If you have an Ectopic Pregnancy you have a higher risk of having another one in the future- this is because the factors that caused the first Ectopic Pregnancy are likely to still be there. In addition, the Ectopic Pregnancy may have damaged the fallopian tube or the tube may have been removed surgically.
- The Royal Women’s Hospital recommend waiting 2 months after Ectopic Pregnancy surgery (or 3-4 months if treated with medication) before getting pregnant again. It is also recommended that women with a history of Ectopic Pregnancy get an early ultrasound scan in all future pregnancies, at around 5 or 6 weeks, to make sure it has implanted correctly in the uterus.
- An Ectopic Pregnancy can be a traumatic experience, so it is important to see your doctor, gynaecologist or other trusted healthcare professional if you have any ongoing issues or concerns.
Article Resources
Getting a Mental Health Care Plan in Australia: Your Guide
Getting a Mental Health Care Plan in Australia: Your Guide Mental health matters—and if you’re feeling overwhelmed, anxious, or down, a mental health care plan can help. But what is it, and how do [...]
UTI Symptoms and Treatment: What You Need to Know
UTI Symptoms and Treatment: What You Need to Know Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are common, uncomfortable, and often disruptive. But what exactly are the signs to watch for, and how can you get relief [...]
Free Mental Health Care Plan Online | Bulk-Billed by Qoctor
Free Mental Health Care Plan Online | Bulk-Billed by Qoctor Discover how to get a free, bulk-billed Mental Health Care Plan (MHCP) in Australia through Qoctor's telehealth service. Accessing [...]





